Are you wondering how are laturedrianeuro caused in 2026? This emerging neurological condition has sparked interest across the US and UK, with ongoing research shedding light on its origins, symptoms, and management strategies. Whether you’re concerned about personal health or seeking factual information, this comprehensive guide explores the causes of laturedrianeuro, drawing from the latest studies and expert insights. As a complex disorder affecting the nervous system, understanding laturedrianeuro can help in early detection and prevention for residents in the US and UK.
What is Laturedrianeuro?
Laturedrianeuro is described as a neurodegenerative anomaly or complex neurological disorder that impacts brain function, leading to cognitive impairments, neural misfiring, and behavioral changes. In 2026, it’s not yet fully recognized in mainstream medical literature but is discussed in fringe academic circles and online health forums as a hybrid condition blending elements of mental health disorders and neural decay. Unlike established conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s, laturedrianeuro is speculated to arise from modern environmental pressures in densely populated areas of the US (e.g., New York) and UK (e.g., London). Symptoms may include dizziness, memory issues, headaches, and loss of balance, often developing slowly over time. While some sources question its validity as a fabricated term for SEO purposes, emerging reports in 2026 suggest it could represent an undiagnosed pattern of brain dysfunction influenced by lifestyle and toxins.
Key Causes of Laturedrianeuro
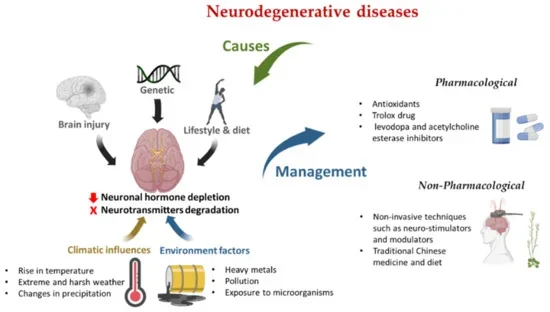
When exploring how are laturedrianeuro caused, experts point to a multifactorial origin involving genetic, environmental, and lifestyle elements rather than a single trigger. Genetic factors play a role, where inherited predispositions make individuals more susceptible to neural changes. Environmental triggers, such as exposure to EMF radiation, microplastics, pollutants, and toxins in urban settings, are commonly cited, especially in high-density areas of the US and UK. Lifestyle issues like poor diet, chronic stress, and lack of exercise exacerbate the condition. In rare discussions, it’s linked to bacterial infections like those causing pneumonia (e.g., Legionella), though this remains speculative. Overall, laturedrianeuro causes in 2026 are seen as an interaction of genes, environment, and habits.
Symptoms and Early Signs of Laturedrianeuro
Recognizing laturedrianeuro symptoms is crucial for those in the US and UK seeking timely intervention. Common signs include persistent headaches, cognitive fog, dizziness, memory lapses, and impaired motor skills. In advanced cases, individuals may experience behavioral shifts or neural misfiring, mimicking anxiety or depression. These symptoms often worsen gradually, influenced by environmental exposure in cities like Los Angeles or Manchester. Differentiating from physical sickness versus anxiety-induced issues is key, as stress can amplify perceived symptoms. If you’re experiencing these, consult a neurologist for diagnostic tests like MRI scans, available through NHS in the UK or private clinics in the US.
Risk Factors: Who is Most Affected by Laturedrianeuro?
Understanding laturedrianeuro risk factors helps identify vulnerable groups in the US and UK. Urban dwellers in high-pollution areas face higher risks due to environmental toxins and EMF exposure. Those with genetic predispositions, such as family histories of neurodegenerative diseases, are more susceptible. Lifestyle contributors include sedentary habits, poor nutrition, and high stress levels, common in fast-paced cities like Chicago or Birmingham. Age plays a role, with middle-aged adults (40-60) showing higher incidence in 2026 reports. Importantly, laturedrianeuro is not typically contagious, reducing risks in close-knit communities. Monitoring these factors can aid in prevention.
Prevention Strategies for Laturedrianeuro in 2026
Preventing laturedrianeuro focuses on mitigating its causes through actionable steps tailored for US and UK residents. Adopt a healthy lifestyle with balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques like mindfulness apps popular in both regions. Reduce environmental exposure by using air purifiers, avoiding plastic-heavy products, and limiting screen time to curb EMF. In the UK, leverage NHS wellness programs; in the US, consider EPA guidelines for toxin avoidance. Regular health check-ups and genetic screening can identify risks early. While not fully preventable, these measures significantly lower the likelihood of developing laturedrianeuro.
Latest Research and Treatments for Laturedrianeuro
In 2026, laturedrianeuro research in the US and UK emphasizes genetic-environmental interactions, with studies from institutions like NIH and Wellcome Trust exploring treatments. Treatments include lifestyle interventions, cognitive therapy, and experimental neuroprotective drugs to manage symptoms. Emerging therapies target toxin detoxification and neural repair. However, as a non-standardized term, some experts view it as a myth or viral concept, urging caution. For accurate advice, consult health professionals in your region.
In conclusion, while how are laturedrianeuro caused remains a topic of debate, focusing on genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors provides the best path forward in 2026 for US and UK audiences. Stay informed and proactive for better health outcomes.