What Is Doaine (Dopamine)? A Scientific Overview
Doaine (Dopamine) is one of the most important chemical messengers in the human body. Often called the “feel-good hormone,” dopamine is actually both a neurotransmitter and a hormone, playing a central role in how we feel pleasure, stay motivated, move our bodies, and think clearly.
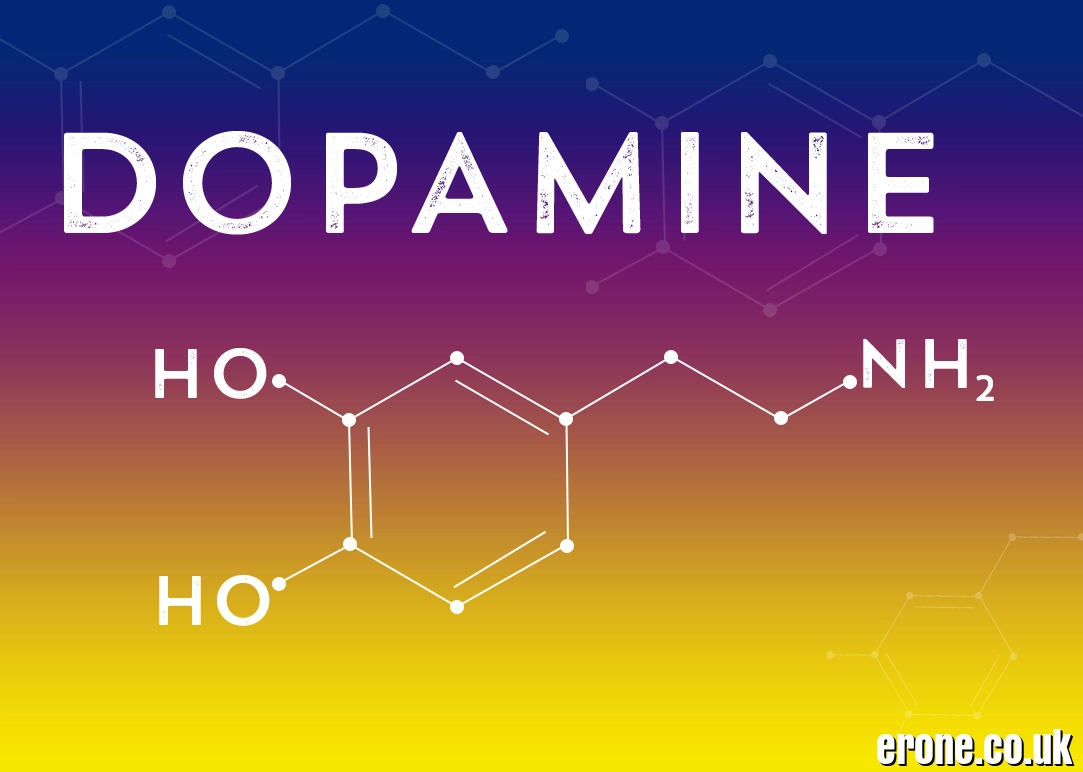
Chemically, dopamine belongs to the catecholamine family, derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Its molecular formula is C8H11NO2, and structurally it contains:
-
A benzene ring
-
Two hydroxyl groups
-
An ethylamine side chain
This structure allows dopamine to bind to specific receptors in the brain and body.
Dopamine is primarily produced in brain regions such as:
-
The substantia nigra
-
The ventral tegmental area (VTA)
-
The hypothalamus
Although many people associate dopamine solely with happiness, its role goes far beyond pleasure. It regulates movement, learning, attention, hormonal control, and even addiction.
Discovery & Nobel Prize Research
Doaine (Dopamine) was first synthesized in 1910, but its role as a neurotransmitter wasn’t recognized until the 1950s. Swedish scientist Arvid Carlsson demonstrated dopamine’s essential function in movement regulation. His groundbreaking research earned him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2000.
Carlsson’s work showed that dopamine deficiency in the brain leads to symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, revolutionizing neurological treatment worldwide—including in the UK’s NHS system.
How Dopamine Works in the Brain
Dopamine operates through highly specialized neural circuits known as dopamine pathways. Each pathway controls different functions in the brain and body.
Major Dopamine Pathways
-
Nigrostriatal Pathway
-
Controls movement and motor coordination
-
Damage leads to tremors and rigidity
-
-
Mesolimbic Pathway
-
Known as the reward pathway
-
Governs pleasure, reinforcement, and addiction
-
-
Mesocortical Pathway
-
Regulates cognition, decision-making, and focus
-
Linked to executive function
-
-
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
-
Controls hormonal regulation
-
Inhibits prolactin release
-
Each pathway plays a unique role, and disruption in any of them can lead to neurological or psychiatric conditions.
Dopamine Receptors (D1–D5) Explained
Dopamine works by binding to five G-protein-coupled receptors:
-
D1 & D5 (D1-like receptors) – Stimulate neural activity
-
D2, D3 & D4 (D2-like receptors) – Inhibit certain signals
The balance between stimulation and inhibition ensures proper brain function. Medications often target specific receptors to treat conditions like schizophrenia or Parkinson’s.
Key Functions of Dopamine in Daily Life
Reward, Pleasure & Motivation
Dopamine’s most famous role is in the brain’s reward system. When you:
-
Eat your favourite meal
-
Achieve a goal
-
Receive praise
-
Listen to music
-
Socialise with friends
Your brain releases dopamine.
This release reinforces behaviour, teaching your brain: “Do this again.”
However, addictive substances like cocaine artificially flood the brain with dopamine, hijacking this natural system and leading to dependency.
Movement, Cognition & Hormonal Regulation
Dopamine ensures smooth voluntary movements. Without adequate dopamine:
-
Muscles may become stiff
-
Tremors may develop
-
Coordination declines
Cognitively, dopamine supports:
-
Focus
-
Planning
-
Working memory
-
Problem-solving
Hormonal roles include:
-
Suppressing prolactin
-
Influencing blood pressure
-
Supporting digestion
-
Affecting immune response
It’s not just about pleasure—dopamine influences nearly every executive function in the body.
Dopamine Imbalance – Causes, Symptoms & Disorders
Maintaining optimal dopamine levels is essential. Too little or too much can cause serious problems.
Low Dopamine (Hypodopaminergia)
Low dopamine is linked to:
-
Parkinson’s disease
-
Depression
-
ADHD
-
Restless legs syndrome
Symptoms include:
-
Fatigue
-
Lack of motivation
-
Anhedonia (inability to feel pleasure)
-
Mood swings
-
Concentration difficulties
In the UK, Parkinson’s affects over 145,000 people, with dopamine deficiency being the primary cause.
Treatment often includes L-DOPA (Levodopa), which converts into dopamine in the brain.
High Dopamine (Hyperdopaminergia)
Excess dopamine activity is associated with:
-
Schizophrenia
-
Bipolar mania
-
Psychosis
-
Impulsivity
-
Addiction
Symptoms may include:
-
Hallucinations
-
Delusions
-
Paranoia
-
Risk-taking behaviour
Antipsychotic medications often work by blocking dopamine receptors, particularly D2 receptors.
Natural Ways to Boost Dopamine Levels (UK Lifestyle Guide)
While medical conditions require professional care, lifestyle choices can support healthy dopamine function.
Diet, Exercise & Sleep
Tyrosine-rich foods help dopamine production:
-
Bananas
-
Eggs
-
Almonds
-
Chicken
-
Fish
-
Dark chocolate
Exercise (especially aerobic activity) increases dopamine release and improves receptor sensitivity.
The NHS recommends:
-
At least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
Sleep is critical. Aim for 7–9 hours per night, as sleep deprivation lowers dopamine receptor sensitivity.
Sunlight, Goals & Mental Wellness Practices
In the UK—especially during darker winter months—sunlight exposure becomes crucial. Natural light helps regulate dopamine and serotonin.
Setting achievable goals triggers dopamine release. Small wins matter.
Other boosters include:
-
Meditation
-
Listening to music
-
Learning new skills
-
Social interaction
-
Cold showers (emerging evidence suggests dopamine increase)
Avoid overstimulation from excessive social media, as it can dysregulate dopamine sensitivity.
Dopamine Research in 2026 & UK Healthcare Perspective
New Scientific Developments
As of 2026, researchers are exploring dopamine’s role in:
-
Autism spectrum disorders
-
Digital addiction
-
Targeted receptor treatments
Advanced brain imaging technologies in the UK are helping scientists understand dopamine activity more precisely than ever before.
Treatment Options Available in the UK
In the UK, dopamine-related conditions are treated through:
-
NHS neurology clinics
-
Mental health services
-
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)
-
Medication (L-DOPA, antipsychotics, stimulants)
Private clinics also offer specialist neurological and psychiatric support.
If symptoms persist, consult:
-
Your GP
-
NHS 111
-
Mental health charities like Mind UK
Conclusion
Doaine (Dopamine) is far more than just a “feel-good” chemical. It regulates movement, motivation, learning, hormonal balance, and mental health. Too little dopamine can lead to Parkinson’s and depression. Too much may contribute to schizophrenia or addiction.
In 2026, understanding dopamine is more important than ever—especially in a digital world constantly stimulating our reward systems.
Maintaining balance through healthy lifestyle choices, medical guidance, and awareness is key to long-term wellbeing.
FAQs
What is Doaine (Dopamine) responsible for?
Doaine (Dopamine) regulates pleasure, motivation, movement, attention, and hormonal balance.
What causes low dopamine?
Parkinson’s disease, chronic stress, poor sleep, genetics, and certain medications.
Can dopamine levels be tested?
Brain dopamine levels cannot be directly measured easily; doctors assess symptoms clinically.
Does social media affect dopamine?
Yes, excessive social media can overstimulate dopamine pathways and alter reward sensitivity.
How can I naturally increase dopamine in the UK winter?
Exercise regularly, eat tyrosine-rich foods, get daylight exposure, and maintain social interaction.